JavaScript Operators
JavaScript operators are symbols that used to perform operations on operands, like in expression ‘8 + 2 = 10’, here 8 and 2 are operands and ‘+’ is operator.
Types of operators in JavaScript:
- Assignment Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
- Conditional (or ternary) Operators
Let’s discuss all the above operators one by one
Assignment Operators
Below are the list of assignment operators in JavaScript:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Assign | 20+20 = 40 |
| += | Add and assign | var x=10; x+=20; Now x = 30 |
| -= | Subtract and assign | var x=20; x-=10; Now x = 10 |
| *= | Multiply and assign | var x=10; x*=20; Now x = 200 |
| /= | Divide and assign | var x=10; x/=2; Now x = 5 |
| %= | Modulus and assign | var x=10; x%=2; Now x = 0 |
Example:
<body>
<script>
var x = 8, y = 12;
document.write(“Value of x is “+x);
document.write(“<br/>Value of y is “+y);
x = y;
document.write(“<br/><br/>Result after x = y : “);
document.write(“<br/>Value of x is “+x);
document.write(“<br/>Value of y is “+y);
x += 1;
document.write(“<br/><br/>Result after x += 1 :”);
document.write(“<br/>Value of x is “+x);
x -= 1;
document.write(“<br/><br/>Result after x -= 1 :”);
document.write(“<br/>Value of x is “+x);
x *= 5;
document.write(“<br/><br/>Result after x *= 5 :”);
document.write(“<br/>Value of x is “+x);
x /= 5;
document.write(“<br/><br/>Result after x /= 5 :”);
document.write(“<br/>Value of x is “+x);
x %= 2;
document.write(“<br/><br/>Result after x %= 2 :”);
document.write(“<br/>Value of x is “+x);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic operations on the operands.
Below are the list of arithmetic operators in JavaScript:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | 10+30 = 40 |
| – | Subtraction | 30-10 = 20 |
| * | Multiplication | 10*10 = 100 |
| / | Division | 20/10 = 2 |
| % | Modulus (Remainder) | 30%15 = 0 |
| ++ | Increment | var x=10; x++; Now x = 11 |
| −− | Decrement | var x=10; x−−; Now x = 9 |
Let’s see working of Arithmetic operators with the help of example:
Example:
<body>
<script type=”text/javascript”>
var a = 12;
var b = 4;
var txt1 = “Good”;
var txt2 = “Day”;
var nextLine = “<br/>”;
document.write(“a + b = “);
result = a + b;
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
document.write(“txt1 + txt2 = “);
result = txt1 + txt2;
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
document.write(“a – b = “);
result = a – b;
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
document.write(“a / b = “);
result = a / b;
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
document.write(“a % b = “);
result = a % b;
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
document.write(“a + b + txt1 = “);
result = a + b + txt1;
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
a = ++a;
document.write(“++a = “);
result = ++a;
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
b = −−b;
document.write(“−−b = “);
result = −−b;
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Comparison Operators
Comparison operators are used to compares the 2 operands.
Below are the list of comparison operators in JavaScript:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| == | Is equal to | 15==30 = false |
| === | Identical (equal and of same type) | 5==15 = false |
| != | Not equal to | 10!=20 = true |
| !== | Not Identical | 40!==40 = false |
| > | Greater than | 20>10 = true |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | 20>=10 = true |
| < | Less than | 20<10 = false |
| <= | Less than or equal to | 20<=10 = false |
Example:
<body>
<script>
var x = 15;
var y = 30;
var nextLine = “<br/>”;
document.write(“Result of (x == y) : “);
result = (x == y);
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
document.write(“Result of (x < y) : “);
result = (x < y);
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
document.write(“Result of (x > y) : “);
result = (x > y);
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
document.write(“Result of (x != y) : “);
result = (x != y);
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
document.write(“Result of (x >= y) : “);
result = (x >= y);
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
document.write(“Result of (x <= y) : “);
result = (x <= y);
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
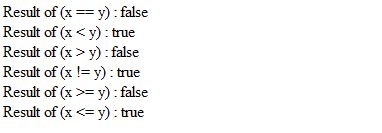
Logical Operators
JavaScript support the below logical operators:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| && | Logical AND | (20==30 && 30==33) = false |
| || | Logical OR | (20==30 || 22==30) = false |
| ! | Logical Not | !(30==25) = true |
Example:
<body>
<script>
var x = true;
var y = false;
var nextLine = “<br />”;
document.write(“Result of (x && y) : “);
result = (x && y);
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
document.write(“Result of (x || y) : “);
result = (x || y);
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
document.write(“Result of !(x && y) : “);
result = (!(x && y));
document.write(result);
document.write(nextLine);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Other Miscellaneous Operator of JavaScript:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| (?:) | This operator is call conditional operator and it returns value based on the condition. It is like if-else. |
| , | Comma Operator allows multiple expressions to be evaluated as single statement. |
| delete | It deletes a property from the object. |
| in | In Operator checks if object has the given property |
| instanceof | checks if the object is an instance of given type |
| typeof | checks the type of object. |
| void | it discards the expression’s return value. |
Example of Conditional Operator (?):
<body>
<script>
var x = 5;
var y = 10;
document.write (‘Result of ((x > y) ? x is greater then y : y is greater then x) : ‘);
result = (x > y) ? ‘x is greater then y’ : ‘y is greater then x’;
document.write(‘<br/>’+result);
</script>
</body>
</html>



